The push for environmental responsibility is reshaping how we move, transforming everything from personal commutes to large-scale resort and community planning. Traditional transportation is a major contributor to global emissions, making the shift to cleaner alternatives more critical than ever. This comprehensive guide moves beyond theory to explore nine pivotal sustainable transportation solutions that offer practical, actionable strategies for individuals, businesses, and entire communities. We will delve into a curated roundup of top-tier options designed for immediate impact.
This article details a range of choices, from advanced street-legal electric vehicles perfect for planned communities to innovative public transit systems and integrated micro-mobility services. To accelerate this transition, understanding policy tools that encourage the adoption of newer, cleaner vehicles is essential. For instance, grasping how scrappage schemes work provides insight into financial incentives designed to remove older, more polluting cars from the road, making way for greener alternatives.
Each solution presented here will be examined for its specific implementation details, real-world impact, and distinct benefits. Our goal is to provide a clear and actionable roadmap for anyone looking to build a more sustainable and efficient transportation ecosystem. Whether you are a resort manager planning a fleet, a community developer designing infrastructure, or an individual seeking a more eco-friendly way to travel, this list offers the insights needed to make informed decisions for a greener future.
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric Vehicles (EVs) represent a monumental shift in personal and commercial transport, replacing traditional internal combustion engines with highly efficient electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries. This fundamental change eliminates tailpipe emissions, making EVs a cornerstone among sustainable transportation solutions, especially for resorts, planned communities, and eco-conscious individuals aiming to reduce their carbon footprint.
The global adoption of EVs showcases their viability. Norway leads the world with an EV market share exceeding 80% for new car sales, demonstrating what's possible with strong incentives and infrastructure. In the commercial sphere, pioneers like Tesla have built a global Supercharger network with over 50,000 stations, while manufacturers such as China's BYD have scaled production to become the world's largest EV maker. This momentum is further solidified by regulatory actions, like California’s mandate for 100% zero-emission vehicle sales by 2035.
Key Performance Metrics for EVs
To better understand their environmental and performance advantages, this infographic summarizes the core benefits of electric vehicles.
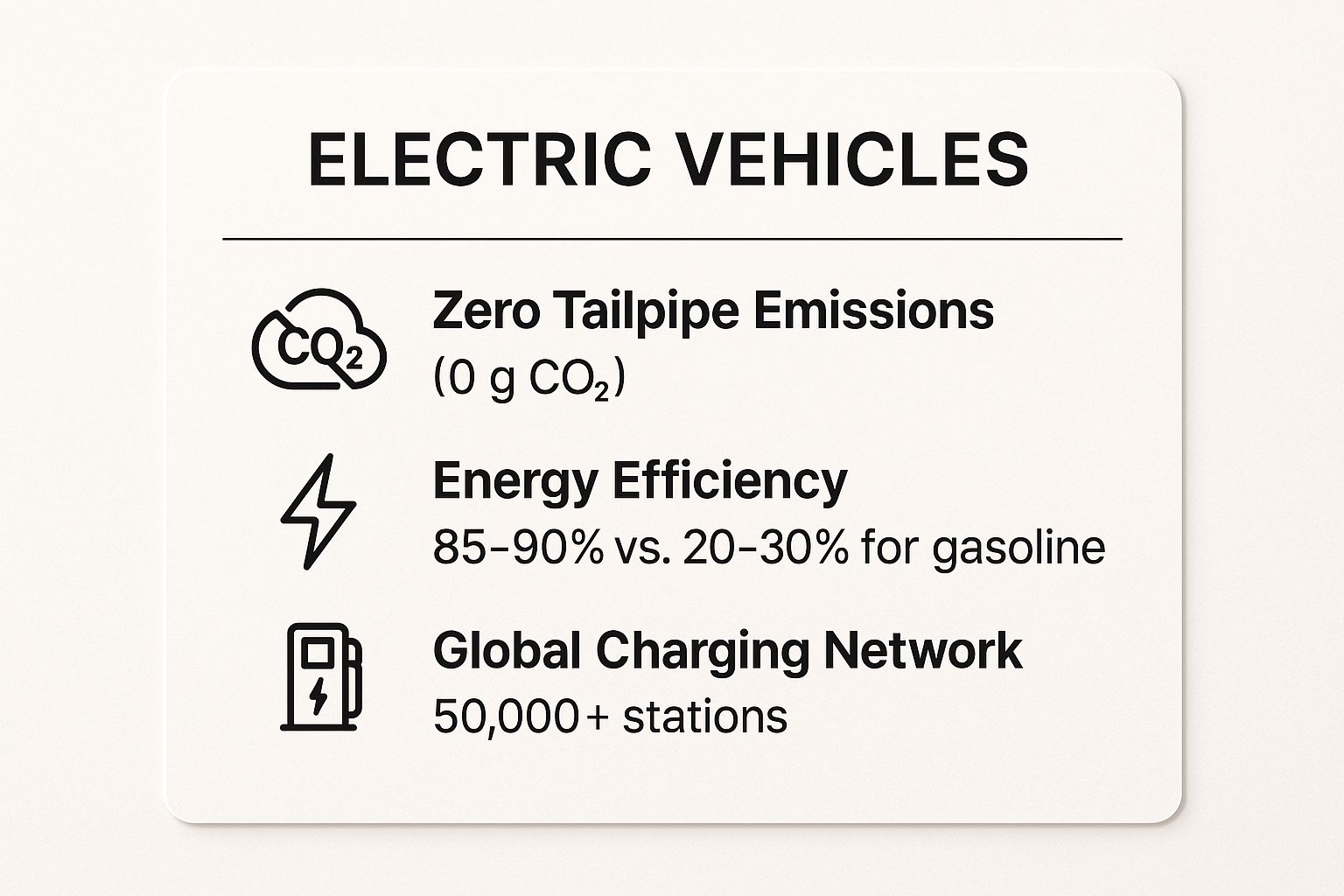
This data highlights the immediate environmental impact of eliminating tailpipe emissions and the significant long-term efficiency gains over gasoline-powered cars.
Practical Implementation and Ownership
For communities, resorts, or individuals, adopting EVs involves more than just the initial purchase. Success relies on strategic planning for charging and understanding the long-term financial benefits.
- Charging Infrastructure: Installing Level 2 charging stations at home or within a community provides convenient, overnight charging. For longer trips, planning routes with apps like PlugShare or A Better Routeplanner is essential.
- Financial Incentives: Governments often offer substantial tax credits and rebates to offset the initial cost. These incentives make EVs more accessible and financially attractive.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): While the sticker price may be higher, EVs typically have lower running costs due to cheaper "fuel" (electricity) and reduced maintenance needs (no oil changes, fewer moving parts). Exploring an in-depth electric vehicle cost comparison can reveal significant long-term savings.
2. Public Transit Systems
Public Transit Systems, encompassing networks of buses, trains, subways, and light rail, are foundational to urban sustainability. These mass transportation solutions efficiently move large populations, drastically reducing per-capita emissions, traffic congestion, and the overall environmental impact of urban mobility. For resorts and planned communities connected to urban centers, leveraging public transit offers a powerful way to enhance guest and resident experiences while promoting green travel.

World-class examples demonstrate the potential of well-designed public transit. Curitiba, Brazil, pioneered the Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) model, creating a high-capacity, cost-effective system that has been replicated globally. In Asia, Singapore’s integrated MRT and bus network provides seamless connectivity, while Tokyo's rail system handles an astonishing 40 million passengers daily with remarkable efficiency. These systems prove that high-quality public transit is a viable and desirable alternative to private car ownership, forming the backbone of sustainable transportation solutions in modern cities.
Key Performance Metrics for Public Transit
To understand its large-scale impact, this infographic summarizes the core benefits of robust public transportation networks.
- Emission Reduction: Reduces CO2 emissions by an average of 45% compared to single-occupancy vehicles.
- Congestion Relief: A full bus can take over 50 cars off the road, while a train can replace hundreds.
- Fuel Savings: Public transit use in the U.S. saves billions of gallons of gasoline annually.
- Land Use Efficiency: Transit-oriented development promotes walkable, dense communities, preserving green space.
This data highlights the immense collective benefit of shifting travel from individual cars to shared, efficient transit systems.
Practical Implementation and Usage
For communities, organizations, and individuals, integrating public transit into daily life requires a strategic approach to maximize convenience and cost-effectiveness.
- Leverage Technology: Use mobile apps like Citymapper or Google Maps for real-time schedules, route planning, and fare information to make journeys predictable and seamless.
- Optimize Fares: For regular commuters, purchasing monthly or annual passes offers significant savings over single-trip tickets. Many systems also offer contactless payment for added convenience.
- Combine Mobility Options: Enhance your journey by using bike-and-ride programs. Many buses and trains are equipped with bike racks, allowing for a flexible commute from the station to your final destination.
- Group Travel Efficiency: For organized group travel, exploring the benefits of minibus hire with a driver for groups can lead to more efficient and sustainable journeys by reducing the number of individual cars on the road.
3. Cycling Infrastructure and Bike-Sharing
Cycling infrastructure and bike-sharing programs represent a powerful, human-scaled approach to sustainable transportation. By creating comprehensive networks of protected bike lanes, paths, and accessible shared bicycle services, communities can promote cycling as a healthy, efficient, and zero-emission mode of transport. This solution is particularly effective for resorts, master-planned communities, and urban centers looking to reduce traffic congestion and improve air quality.

The global success of this model is evident in cities renowned for their livability. Copenhagen, a city where nearly 50% of residents commute by bike, serves as a prime example of what dedicated infrastructure can achieve. Similarly, the Netherlands boasts over 35,000 km of cycling paths, making it one of the safest and easiest places to cycle in the world. In Paris, the Vélib' bike-sharing system offers over 20,000 bikes, seamlessly integrating with public transit and encouraging short-distance, sustainable trips.
Key Performance Metrics for Cycling
To better understand its environmental and community advantages, this infographic summarizes the core benefits of robust cycling infrastructure.
This data underscores the immediate public health benefits of active transport and the significant reduction in urban noise and air pollution.
Practical Implementation and Adoption
For communities or resorts, fostering a cycling culture requires a strategic investment in both infrastructure and accessibility. For individuals, adopting cycling is about building confidence and utilizing available resources.
- Infrastructure Development: Prioritizing the creation of physically separated bike lanes is crucial for safety and encouraging adoption among all age groups. Well-marked routes and secure bike parking at key destinations are also essential components.
- Bike-Sharing Programs: Implementing a bike-share system, like New York's Citi Bike, provides residents and visitors with convenient, on-demand access to bicycles without the need for personal ownership. Apps make it easy to locate and unlock bikes.
- Safety and Education: Promoting safety through community workshops and ensuring riders are equipped with helmets and lights is vital. Individuals can start with short, familiar routes to build confidence before tackling longer commutes.
- Local Advocacy: Residents can play a key role by advocating for better cycling infrastructure in their local communities, pushing for policies that prioritize active transportation as one of the most effective sustainable transportation solutions.
4. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (HFCVs) offer a compelling vision for the future of sustainable transportation solutions, using a sophisticated electrochemical process to power an electric motor. Instead of storing electricity in a battery, HFCVs generate it onboard by combining hydrogen gas from a tank with oxygen from the air. This reaction produces electricity, heat, and water vapor as the only byproduct, completely eliminating harmful tailpipe emissions. This technology is particularly promising for users needing long range and rapid refueling, similar to conventional gasoline vehicles.
The adoption of HFCVs is growing, led by pioneering efforts in specific regions. Japan has established over 160 hydrogen refueling stations to support its growing fleet, while California’s "hydrogen highway" initiative aims to build a comprehensive network of stations. Automakers like Toyota have advanced the market with models like the Mirai, which has sold over 20,000 units globally, and Hyundai continues to innovate with its NEXO fuel cell SUV. These real-world applications demonstrate the technology's potential for both personal and commercial use.
Practical Implementation and Ownership
For those considering HFCVs, successful adoption hinges on understanding the unique infrastructure requirements and available support systems. While not as widespread as EV charging, the hydrogen network is expanding.
- Refueling Infrastructure: Prospective owners must first research the availability of hydrogen refueling stations in their area. Apps and websites from organizations like the California Fuel Cell Partnership provide real-time maps of operational stations.
- Financial Incentives: Similar to EVs, government incentives and manufacturer rebates are often available to help lower the initial purchase or lease price. Leasing is a popular option, frequently including a fuel allowance.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating an HFCV, it is crucial to consider the complete cost profile. This includes the vehicle price, government rebates, and the cost of hydrogen fuel, which can vary by location but is becoming more competitive.
5. Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF)
Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) represent a critical innovation for decarbonizing air travel, one of the most challenging sectors for emission reduction. Produced from renewable sources like waste oils, agricultural residues, algae, and synthetic fuels, SAF is a "drop-in" solution that can be blended with conventional jet fuel and used in existing aircraft engines without modification. This makes it one of the most promising sustainable transportation solutions for minimizing the aviation industry's significant carbon footprint.
The global aviation industry is actively embracing SAF to meet ambitious climate goals. United Airlines has made a landmark commitment to purchase 3.4 billion gallons of SAF, while KLM operated the world's first commercial flight using biofuel from used cooking oil. Further demonstrating its viability, Singapore Airlines has integrated SAF into its operations at Changi Airport, and British Airways is investing in a waste-to-jet-fuel facility. These initiatives, supported by producers like Neste and championed by organizations like the International Air Transport Association (IATA), prove SAF is a scalable and effective strategy.
Practical Implementation and Support
While individual travelers cannot directly purchase SAF, they can influence its adoption and mitigate their travel footprint through informed choices and advocacy. Supporting this transition is key to making air travel more sustainable.
- Choose Airlines with SAF Commitments: When booking flights, prioritize carriers that have publicly invested in SAF programs. Many leading airlines now highlight their sustainability efforts on their websites.
- Advocate for Incentives: Support government policies and incentives that encourage the production and lower the cost of SAF, making it more competitive with traditional jet fuel.
- Participate in Carbon Offset Programs: Many airlines offer programs where passengers can pay a small extra fee to offset the carbon emissions of their flight, often by investing in renewable energy projects or SAF development.
- Stay Informed: Follow the work of aerospace leaders like Boeing and Airbus, who are instrumental in testing and certifying aircraft for 100% SAF usage, pushing the industry toward a fully sustainable future.
6. Electric Public Transit
Electric public transit electrifies mass mobility, replacing diesel-powered buses, trams, and trains with emissions-free alternatives powered by electricity. This transition is a critical component of creating sustainable transportation solutions for urban environments, resorts, and large-scale planned communities. By moving large numbers of people efficiently and without tailpipe emissions, electric transit systems dramatically reduce a city's carbon footprint and improve local air quality.
The global shift towards electric mass transit is already well underway. The city of Shenzhen, China, famously operates a fleet of over 16,000 electric buses, creating one of the world's quietest and cleanest urban transportation networks. Similarly, cities like London and Los Angeles are aggressively phasing out diesel buses in favor of electric models, while Oslo, Norway, is on a path to make its entire public transport system fully electric. These examples prove the model is scalable, reliable, and environmentally transformative.
Key Benefits of Electric Transit
Electrifying public transportation offers compounding benefits that extend beyond just reducing emissions. This infographic breaks down the core advantages for communities and transit authorities.
This data underscores how electric transit not only cleans the air but also creates a quieter, more pleasant urban experience and offers significant operational savings over time.
Practical Implementation and Support
For communities, supporting and integrating electric public transit involves both advocacy and practical action. Success hinges on robust infrastructure and strong public engagement to maximize ridership and benefits.
- Advocacy and Funding: Support local and national initiatives that fund the transition to electric buses and light rail. Advocating for charging infrastructure to be powered by renewable energy sources further amplifies the environmental benefits.
- Rider Optimization: Use public transit apps to plan trips, track vehicle locations in real-time, and make multimodal journeys seamless. This encourages higher ridership and reduces reliance on personal vehicles.
- Fleet Management: The operational backbone of these systems is sophisticated management. Transit authorities must handle complex charging schedules, route optimization, and maintenance, a process that shares principles with commercial fleet operations. For more on this, see this guide to electric vehicle fleet management.
- Provide Feedback: Actively communicate with local transit authorities. Feedback on route efficiency, service frequency, and vehicle quality helps them improve the system for everyone.
7. Walkable Urban Design
Walkable Urban Design is a foundational strategy among sustainable transportation solutions, focusing on creating environments where daily needs are accessible on foot. This approach prioritizes people over cars by integrating mixed-use development, compact community layouts, and "complete streets" that are safe for pedestrians and cyclists. For resorts, planned communities, and municipalities, this design philosophy reduces reliance on vehicles, lowers emissions, and promotes healthier, more active lifestyles.
The global impact of pedestrian-centric planning is significant. Barcelona’s innovative "superblocks" reroute traffic to create pedestrian-priority zones, resulting in a 32% reduction in local traffic and improved air quality. Similarly, Copenhagen transformed its city center into a vast pedestrian-friendly area, while Portland, Oregon, has become a leader in transit-oriented development, concentrating housing and services around public transport hubs. These examples, championed by urbanists like Jane Jacobs and Jan Gehl, prove that designing for walkability is a powerful tool for sustainability.
Key Performance Metrics for Walkable Design
To better understand its environmental and social advantages, this infographic summarizes the core benefits of walkable urban design.
This data highlights how thoughtful urban planning can drastically reduce vehicle miles traveled and foster a stronger sense of community and well-being.
Practical Implementation and Advocacy
For communities and property developers, implementing walkable design involves strategic planning and community engagement. Success depends on shifting the focus from accommodating cars to creating human-scaled environments.
- Advocate for Complete Streets: Support local policies that require streets to be designed for all users, including pedestrians, cyclists, and transit riders, not just drivers. This includes adding sidewalks, bike lanes, and safe crosswalks.
- Support Mixed-Use Zoning: Champion development projects that mix residential, commercial, and recreational spaces. This allows residents to live, work, and play without needing a car for every trip.
- Engage in Local Planning: Participate in town hall meetings and planning commissions to voice support for pedestrian-friendly infrastructure. Use walkability assessment tools to provide data-driven recommendations for your neighborhood.
8. Car-Sharing and Mobility-as-a-Service
Car-Sharing and Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms represent a paradigm shift from vehicle ownership to on-demand access. These integrated services provide users with a flexible, cost-effective way to utilize various transportation modes, including shared cars, bikes, scooters, and public transit, often through a single unified app. By reducing the need for private vehicle ownership, these models directly combat urban congestion and parking scarcity, making them powerful sustainable transportation solutions for resorts, dense communities, and eco-conscious urbanites.
The global success of these models underscores their effectiveness. Zipcar operates in over 500 cities, demonstrating the viability of station-based car-sharing, while Car2Go (now SHARE NOW) pioneered the free-floating model, allowing users to pick up and drop off vehicles anywhere within a service area. On a broader scale, Helsinki's MaaS Global "Whim" app integrates all local transport options into one subscription service, offering a true alternative to owning a car.
Key Performance Metrics for Car-Sharing and MaaS
To better understand the environmental and practical advantages, this infographic summarizes the core benefits of adopting shared mobility services.
This data highlights how shared mobility reduces the total number of vehicles on the road, directly lowering emissions, resource consumption, and the urban space required for parking.
Practical Implementation and Usage
For communities or individuals, leveraging car-sharing and MaaS effectively requires a slight shift in mindset from ownership to access. Strategic use can maximize convenience and savings.
- Platform Integration: Choose a MaaS platform that integrates multiple transport options. This allows you to seamlessly combine a shared car for a grocery run with an e-scooter for the final leg of your journey.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Compare membership tiers against your expected usage. A pay-per-use model may suit infrequent drivers, while a monthly subscription can offer better value for regular users. For trips requiring more traditional vehicle access, checking various car rental locations can supplement a shared mobility plan.
- Community Fleets: Planned communities and resorts can establish their own shared fleets, often featuring vehicles like the versatile and eco-friendly models detailed in this guide to road-legal electric carts. This provides residents and guests with convenient, on-site transportation without the hassle of personal vehicle ownership.
9. High-Speed Rail
High-Speed Rail (HSR) systems are advanced electric-powered passenger trains that operate at speeds often exceeding 200 mph (320 km/h). By connecting major cities with fast, efficient, and reliable service, HSR presents a powerful sustainable transportation solution that significantly reduces reliance on short-haul flights and personal vehicle travel. This mode of transport dramatically cuts down on carbon emissions per passenger, making it an essential component of modern, green infrastructure.
The global success of HSR demonstrates its transformative potential. Japan’s Shinkansen, operational for nearly 60 years, is a benchmark for safety and punctuality. Similarly, France’s TGV network has reshaped European travel, while China has built the world's most extensive HSR network, spanning over 40,000 kilometers. These systems prove that high-speed rail can effectively replace less sustainable travel options for intercity journeys, offering a comfortable and low-stress alternative to congested airports and highways.
Key Performance Metrics for High-Speed Rail
High-speed rail offers compelling environmental and efficiency benefits compared to other forms of long-distance travel.
This data underscores HSR's superior energy efficiency and its role in reducing the carbon footprint associated with medium-distance travel.
Practical Implementation and Advocacy
For travelers and communities, embracing high-speed rail involves both using existing services and supporting future development. Its integration into regional planning is key to maximizing its benefits.
- Smart Travel Planning: When traveling between cities connected by HSR, book tickets in advance for significant cost savings. Consider purchasing rail passes if you plan multiple trips within a country or region.
- Support Infrastructure Growth: Advocate for public and private funding for new HSR projects. Supporting initiatives like the California High-Speed Rail Authority can help expand sustainable transportation networks.
- Integrated Transit: Promote integrated transportation planning that connects HSR stations with local public transit, bike-sharing, and other micro-mobility solutions to create a seamless, car-free travel experience.
Sustainable Transportation Solutions Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Moderate: requires charging network | High: batteries, charging infrastructure | Reduced emissions, lower operating costs | Personal transport, urban and suburban use | Zero tailpipe emissions, instant torque, low maintenance |
| Public Transit Systems | High: infrastructure & operationally complex | Very high: vehicles, stations, infrastructure | Large-scale emission reduction, congestion relief | Urban mass transit, reducing car dependency | High capacity, cost-effective, social equity |
| Cycling Infrastructure & Bike-Sharing | Low to Moderate: infrastructure expansion needed | Low: bike lanes, bike-share stations | Zero emissions, health benefits | Short-distance urban travel, first/last mile trips | Zero emissions, low cost, traffic reduction |
| Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles | High: tech advanced, fueling stations needed | High: hydrogen production, storage, fueling | Zero emissions, long range, quick refueling | Long-range travel, heavy-duty vehicles | Long range, fast refueling, zero emissions |
| Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) | High: complex supply chain & certification | High: production facilities, feedstock sourcing | Up to 80% lifecycle emission reduction | Aviation industry, drop-in jet fuel replacement | Large emission reductions, no aircraft mods |
| Electric Public Transit | High: electrification & infrastructure | Very high: vehicles, overhead wires, batteries | Zero emissions, improved urban air quality | Urban bus, tram, metro systems | Zero tailpipe emissions, lower noise & maintenance |
| Walkable Urban Design | High: urban redevelopment & policies | Moderate to High: planning, street design | Reduced vehicle use, increased physical activity | Urban planning for healthy, active communities | Reduces VMT, promotes health & community |
| Car-Sharing & Mobility-as-a-Service | Moderate: digital platform + fleet management | Moderate: fleet, app development | Reduced private vehicle ownership, flexible use | Urban mobility, reducing parking demand | Optimizes vehicle use, reduces ownership costs |
| High-Speed Rail | Very High: dedicated tracks & systems | Very high: rail construction, technology | Efficient long-distance travel, low emissions | Intercity travel, alternatives to short flights | High speed, high capacity, reliable |
Driving Forward: Integrating Sustainable Mobility into Your World
The journey toward a greener future is paved not with a single path, but with a complex and interconnected network of sustainable transportation solutions. As we have explored, the transition away from fossil-fuel-dependent mobility is a multifaceted endeavor, requiring a blend of personal choices, community planning, and technological innovation. From the quiet efficiency of personal electric vehicles to the collective power of enhanced public transit and the forward-thinking design of walkable communities, each solution represents a vital piece of a larger environmental puzzle.
The options detailed in this article, spanning everything from high-speed rail to advanced Sustainable Aviation Fuels, illustrate that there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Instead, the most effective strategy involves creating a rich, diverse transportation ecosystem where different modes work in harmony. For an individual, this might mean combining cycling for short trips with an EV for longer commutes. For a resort manager or community planner, it involves integrating shared mobility services and creating infrastructure that prioritizes people over cars.
Key Takeaways for a Sustainable Future
Recapping our exploration, several core principles emerge as critical for accelerating this transition. These are the actionable insights that turn broad concepts into tangible progress for both individuals and organizations.
- Diversification is Essential: Relying on a single solution is a flawed strategy. The most resilient and effective transportation networks integrate multiple options, such as EVs, bike-sharing, robust public transit, and walkable infrastructure, to meet diverse needs.
- Infrastructure is the Foundation: The success of nearly every sustainable option, from cycling to electric vehicles, hinges on supportive infrastructure. This includes dedicated bike lanes, widespread and reliable EV charging stations, and well-planned public transit routes.
- Policy and Planning Drive Adoption: Individual choices are powerful, but systemic change requires deliberate policy and urban planning. Prioritizing funding for electric public transit, zoning for mixed-use developments, and investing in high-speed rail are crucial government-led actions.
- Micro-Mobility Fills a Critical Gap: Solutions like e-bikes and shared scooters are not novelties; they are essential for solving the "last-mile" problem. They connect people to public transit hubs and reduce reliance on cars for short, everyday trips.
Your Next Move: Implementing Change Today
Understanding these concepts is the first step; the next is implementation. For eco-conscious consumers, this could mean researching your next vehicle purchase with an electric model in mind or advocating for better cycling infrastructure in your town. For resort operators, gated community managers, or golf cart dealerships, the opportunity is even more direct and impactful.
The most significant impact often comes from localized, targeted action. By transforming how people move within a defined community or property, you create a microcosm of sustainable living that can inspire broader change.
This is where specialized, low-speed vehicles (LSVs) become a cornerstone of practical sustainability. They offer an immediate way to decarbonize internal transport, reduce noise pollution, and lower long-term operational and fuel costs. These vehicles are not just an amenity; they are a powerful statement of environmental commitment and operational intelligence. By embracing these readily available sustainable transportation solutions, you can lead by example, demonstrating that a cleaner, quieter, and more efficient mode of transport is not a distant dream but a present-day reality. The path forward is clear: it requires a collective commitment to adopt, integrate, and champion the diverse technologies and strategies at our disposal, starting right where we live and work.
Ready to implement a practical, powerful, and stylish sustainable transportation solution for your community, resort, or personal use? Explore the premium lineup of street-legal electric vehicles at Solana EV. Discover how our advanced, eco-friendly models can elevate your transportation experience while contributing to a cleaner planet at Solana EV.
